Transforming Cassava Waste into Prebiotic Fiber: A Novel Resistant Maltodextrin (RMD) from Cassava Pulp
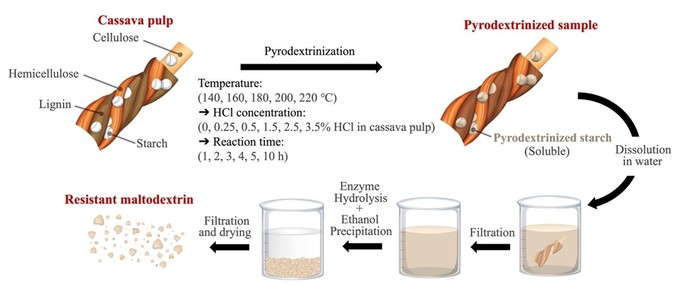 |
This research successfully developed resistant maltodextrin (RMD) from the remaining starch in cassava pulp using pyrodextrinization and enzymatic hydrolysis. Under optimal conditions (180°C, 0.5% HCl, 5 h), the process yielded 18.6% RMD, featuring irregular sponge-like particles and a predominantly DP 15–16 molecular size (70.9%). Structural analysis confirmed the loss of crystalline starch, the presence of β-glycosidic and indigestible linkages, and a high digestion-resistant fraction (91.7%), making it a promising dietary fiber source. Notably, RMD exhibited prebiotic potential by stimulating the growth of four probiotic species.
This research highlights cassava pulp as a valuable resource for producing RMD, offering sustainable applications in functional food development.
#CassavaInnovation #PrebioticFiber #SustainableFood #FoodScience
